Recycled plastic is reshaping drinkware design, offering eco-friendly options for water bottles, tumblers, and more. Here's why it matters:
- Consumer Demand: Over 60% of U.S. shoppers prefer products made from recycled materials, with nearly 70% willing to pay extra.
- Environmental Impact: Using recycled PET (rPET) can cut carbon emissions by up to 79% compared to new plastic.
-
Material Types: Two main plastics dominate drinkware production:
- rPET: Lightweight, clear, and safe for food use.
- Recycled HDPE: Durable, chemical-resistant, and ideal for reusable items.
- Production Process: From collection to molding, strict quality control ensures safety and performance.
- Challenges: Material inconsistencies, supply chain issues, and durability concerns require ongoing innovation.
Brands like BLENDi are leading the charge by using rPET and modular designs to create durable, multi-functional products. As recycling technology improves, the future of drinkware design will see a stronger focus on reducing waste while delivering high-quality products.
How to make 100% RECYCLED Tumblers
Types of Recycled Plastics Used in Drinkware
Recycled materials are playing an increasingly important role in drinkware production, with manufacturers gravitating toward two key types of recycled plastics. These materials showcase the adaptability of recycled plastics in creating functional and sustainable products.
rPET (Recycled Polyethylene Terephthalate)
rPET is a widely used recycled plastic, primarily derived from post-consumer items like water bottles, soda bottles, and food containers. These discarded items are transformed into new drinkware, promoting environmentally conscious design.
What makes rPET stand out is its combination of lightweight strength and shatter resistance. Its clarity rivals that of virgin plastic, making it both practical and visually appealing. Additionally, rPET meets FDA standards for food contact, ensuring it is safe for repeated beverage use.
Environmentally, the benefits of rPET are hard to ignore. Compared to virgin PET, rPET production can cut greenhouse gas emissions by up to 79%. It also consumes up to 60% less energy than creating new plastic from raw materials.
Recycled HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene)
Recycled HDPE comes from sources like milk jugs, detergent bottles, and similar products. While it lacks the transparency of rPET, it compensates with exceptional durability and resistance to chemicals, making it a strong contender in eco-friendly drinkware.
Its high strength-to-density ratio makes recycled HDPE ideal for tough, reusable drinkware that can handle daily use. Another advantage is its resistance to absorbing flavors and odors, making it perfect for holding various beverages. Like rPET, recycled HDPE undergoes rigorous cleaning and testing to meet FDA food-contact standards.
| Property | rPET (Recycled PET) | Recycled HDPE |
|---|---|---|
| Source Material | Beverage bottles, food containers | Milk jugs, detergent bottles |
| Key Properties | Lightweight, clear, strong, food-safe | Opaque, durable, chemical-resistant |
| Common Applications | Water bottles, tumblers, cups | Reusable bottles, cups, lids |
| Food Contact Approval | FDA-approved (with conditions) | FDA-approved (with conditions) |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces GHG emissions, high recycled content | Long lifespan, recyclable |
In the United States, over 1.8 billion pounds of PET bottles are recycled annually. Both rPET and recycled HDPE demonstrate how recycled plastics can deliver safety, performance, and environmental advantages in drinkware, meeting consumer expectations while supporting sustainability efforts.
How Recycled Plastic Becomes Portable Drinkware
Transforming plastic waste into durable, food-safe drinkware involves a detailed process that adheres to strict U.S. standards.
Collection and Sorting of Plastic Waste
The journey begins with collecting plastic waste from post-consumer and industrial sources. These facilities handle millions of pounds of plastic annually, ensuring proper separation to maintain material quality and prevent contamination. Advanced technologies like optical scanners and density separation systems are used to classify plastics, such as PET, HDPE, and polypropylene.
Color sorting plays a critical role, as clear plastics are more versatile and command higher market value. In contrast, dark or colored plastics often require unique processing methods, which can limit design options for the final product. Labels, adhesives, and food residue must also be removed during this phase to avoid quality issues later in the production process.
Once sorted and cleaned, the material is ready for the next stage of manufacturing.
Recycling and Manufacturing Processes
After sorting, the plastic waste undergoes an intensive cleaning process. Industrial washing systems remove labels, adhesives, and any leftover residues. The cleaned plastic is then shredded and granulated into small flakes, which are washed again and heated to eliminate volatile compounds and lingering contaminants.
Next, the material is melted and extruded into uniform pellets. These pellets are then shaped into drinkware using methods like injection molding, blow molding, or thermoforming. Emerging technologies, such as depolymerization, are pushing the boundaries of recycling by breaking plastics down to their base monomers. This innovation allows even hard-to-recycle materials, like ocean plastics or colored plastics, to be transformed into high-quality, food-safe drinkware materials.
| Step | Description | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Collection & Sorting | Gathering and separating plastics by type and color | Maintains material purity |
| Cleaning & Shredding | Washing and shredding plastics into granules | Removes contaminants |
| Granulation | Breaking down plastics into uniform pellets | Prepares material for molding |
| Molding | Shaping plastics via extrusion or other methods | Defines the final product shape |
| Cooling & Trimming | Rapid cooling and precise trimming | Ensures uniformity and quality |
| Quality Control | Inspecting for defects and regulatory compliance | Meets safety standards |
These steps are followed by rigorous quality control to ensure the drinkware meets safety and performance standards.
Ensuring Quality and Compliance
To comply with U.S. FDA regulations for food-contact materials, manufacturers implement stringent quality control measures throughout production. This includes extensive chemical safety testing, such as migration tests, to confirm that harmful substances won't leach into beverages.
Recycled food-contact plastics must meet strict FDA requirements, including limits on contaminants and migration. Each batch undergoes thorough inspections to identify defects that could compromise safety or functionality.
However, variability in source materials remains a challenge. Differences in plastic types, contamination levels, and supply chain inconsistencies can impact the strength, appearance, and safety of the final product. This makes robust sorting, cleaning, and testing protocols essential.
Closed-loop recycling systems are increasingly being adopted to address these challenges. By controlling the entire supply chain - from collection to production - manufacturers can achieve more consistent quality and performance in recycled plastic drinkware.
An example of this approach is BLENDi, which demonstrates how recycled plastics can be used to create portable drinkware without sacrificing quality or safety.
Benefits of Recycled Plastic in Portable Drinkware
Using recycled plastic in portable drinkware helps cut down on waste while building trust with consumers. These advantages touch on both environmental responsibility and market appeal. Here's a closer look at how these benefits serve both the planet and consumer brands.
Benefits for the Planet
Recycled plastic offers clear environmental advantages by reducing landfill waste and keeping materials in circulation. Unlike virgin materials, producing drinkware from recycled plastic uses less petroleum and natural gas, which helps conserve natural resources by limiting the need for drilling and mining. The manufacturing process also requires less energy, leading to fewer greenhouse gas emissions - a step forward in addressing climate change.
This approach supports a circular economy, where materials are collected, processed, and reused in a continuous loop. By maximizing resource efficiency, recycled plastic helps create a more sustainable production cycle, reducing the environmental impact of disposable items.
Consumer and Brand Benefits
The benefits of recycled plastic extend beyond environmental impact, resonating strongly with today's eco-conscious shoppers. In the U.S., more consumers are actively seeking products that align with their environmental values, driving demand for drinkware made from recycled materials. For brands, using recycled plastic signals a commitment to sustainability, which can strengthen trust and loyalty among customers. This is particularly important as U.S. sustainability goals and regulations push companies toward greener practices.
Experts in materials science and sustainability emphasize the importance of recycled plastics in reducing the environmental footprint of consumer goods. Thanks to advances in recycling technology, it's now possible to create high-quality, durable drinkware from recycled materials - making sustainable design scalable and practical.
In a competitive market, products made from recycled plastic empower consumers to make environmentally responsible choices without compromising on quality or functionality. Shoppers are encouraged to look for clear labeling, third-party certifications (such as those verifying rPET content), and transparency about sourcing and production methods. Supporting brands like BLENDi, which prioritize recycled materials and sustainability, can help drive broader industry adoption of eco-friendly practices.
The combined environmental and consumer benefits make a strong case for incorporating recycled plastic into portable drinkware. As recycling technology continues to improve, the potential for even greater impact grows.
sbb-itb-75eb6cf
Challenges in Designing Recycled Plastic Drinkware
Recycled plastic offers a more sustainable option, but it comes with its own set of technical hurdles when used for drinkware. These challenges span everything from material inconsistencies to supply chain complexities, requiring ongoing advancements in design and production.
Material Variability and Durability
One of the biggest challenges with recycled plastic drinkware is its unpredictable appearance. Unlike virgin plastics, which deliver consistent color and texture, recycled materials often show speckling, uneven coloring, or visible impurities. These issues can impact how customers perceive the product and even affect the brand's image. What’s more, these inconsistencies can occur even within a single batch, as the feedstock comes from various sources.
Durability is another major concern. Recycled plastics tend to have weaker polymer chains due to prior use and processing. This degradation can reduce impact resistance and lead to a mechanical strength that’s up to 20% lower than virgin plastics. Such weaknesses make it harder to ensure that drinkware can handle everyday wear and tear, like being dropped or exposed to extreme temperatures. Additionally, leftover contaminants or odors from previous uses can compromise food safety and the overall user experience.
Some manufacturers address these issues by blending recycled plastics with virgin materials, using compatibilizers, or reinforcing their designs for added strength. Research into advanced recycling methods, like chemical recycling, also shows potential for creating higher-quality recycled resins that could solve many of these problems.
Quality Control and Supply Chain Issues
The variability in recycled materials doesn’t just affect durability - it also creates headaches for supply chains. In the U.S., the recycling system is fragmented, making it hard for manufacturers to source consistent, high-quality recycled materials. Differences in local recycling standards, collection methods, and limited processing infrastructure all contribute to supply chain disruptions, material inconsistencies, and increased costs. To make matters worse, only about 8.7% of plastics in the U.S. were recycled in 2021, leaving manufacturers with a limited supply of recycled feedstock for drinkware production.
Supply chain challenges are further compounded by contamination from non-recyclable materials and competition across industries for the same recycled resources. These factors can cause delays, drive up production costs, or force manufacturers to mix in virgin polymers to maintain quality. For instance, in June 2023, WaterBottle.Tech revealed that their ocean plastic water bottles had a defect rate 15% higher than those made from post-consumer rPET. The issues stemmed from color and texture inconsistencies, as well as the extra cleaning required for ocean plastics.
Meeting FDA regulations adds another layer of complexity. Recycled plastics used in drinkware must pass rigorous testing to ensure they’re safe for food contact. The variability and unknown origins of recycled feedstock make compliance particularly challenging, often requiring additional certifications and documentation.
To tackle these hurdles, manufacturers can invest in advanced sorting and cleaning technologies, enforce strict quality control measures, and work with certified suppliers to ensure consistent, safe materials. Clear communication with consumers about the challenges and benefits of recycled plastic drinkware can also help set realistic expectations and build trust.
For brands like BLENDi, navigating these supply chain and quality issues is crucial to delivering reliable, eco-conscious products. Striking the right balance between durability, visual appeal, and sustainability demands constant innovation in both material selection and manufacturing processes.
New Trends in Eco-Friendly Drinkware Design
The drinkware industry is undergoing a big shift as manufacturers turn to more sustainable practices, especially in how they use recycled plastics. These changes aim to tackle environmental concerns while overcoming technical challenges that have slowed the adoption of recycled materials in the past. Two key trends leading this transformation are the use of ocean plastics and the growing reliance on post-consumer rPET.
Using Ocean Plastics and Post-Consumer rPET
Ocean plastic recovery is making waves in sustainable drinkware. Companies are now collecting plastics from coastal waterways and ocean cleanup projects, transforming waste into high-quality drinkware. These efforts have removed over 1,000 metric tons of plastic waste while also providing income to local collectors. Many of these products are designed with modular features, allowing users to replace parts like lids or seals, which extends their lifespan. Plus, they remain dishwasher-safe, making them practical for everyday use.
The adoption of post-consumer rPET is another game-changer. Unlike industrial scrap, post-consumer materials come directly from household recycling programs, making a bigger dent in environmental issues. Some manufacturers have introduced product lines made entirely from post-consumer rPET, cutting carbon footprints by up to 60% compared to using virgin plastics. Many brands are also increasing the recycled content in their products by 30%, signaling a strong commitment to sustainability.
New technologies are also improving how recycled plastics are processed. For example, depolymerization technology can now turn even colored or ocean plastics into food-grade drinkware. This solves a long-standing issue where colored or contaminated plastics couldn’t be converted into clear, safe drinking vessels.
Modular designs are another smart innovation. By allowing users to replace specific parts - like straws, seals, or lids - these designs extend the life of the product and make recycling easier. Components can be separated by material type, simplifying the recycling process at the end of the product's life.
Transparency is also becoming a major selling point. Consumers increasingly want to know exactly how much recycled content is in their products, and brands are responding by clearly labeling materials and percentages.
BLENDi's Commitment to Sustainability
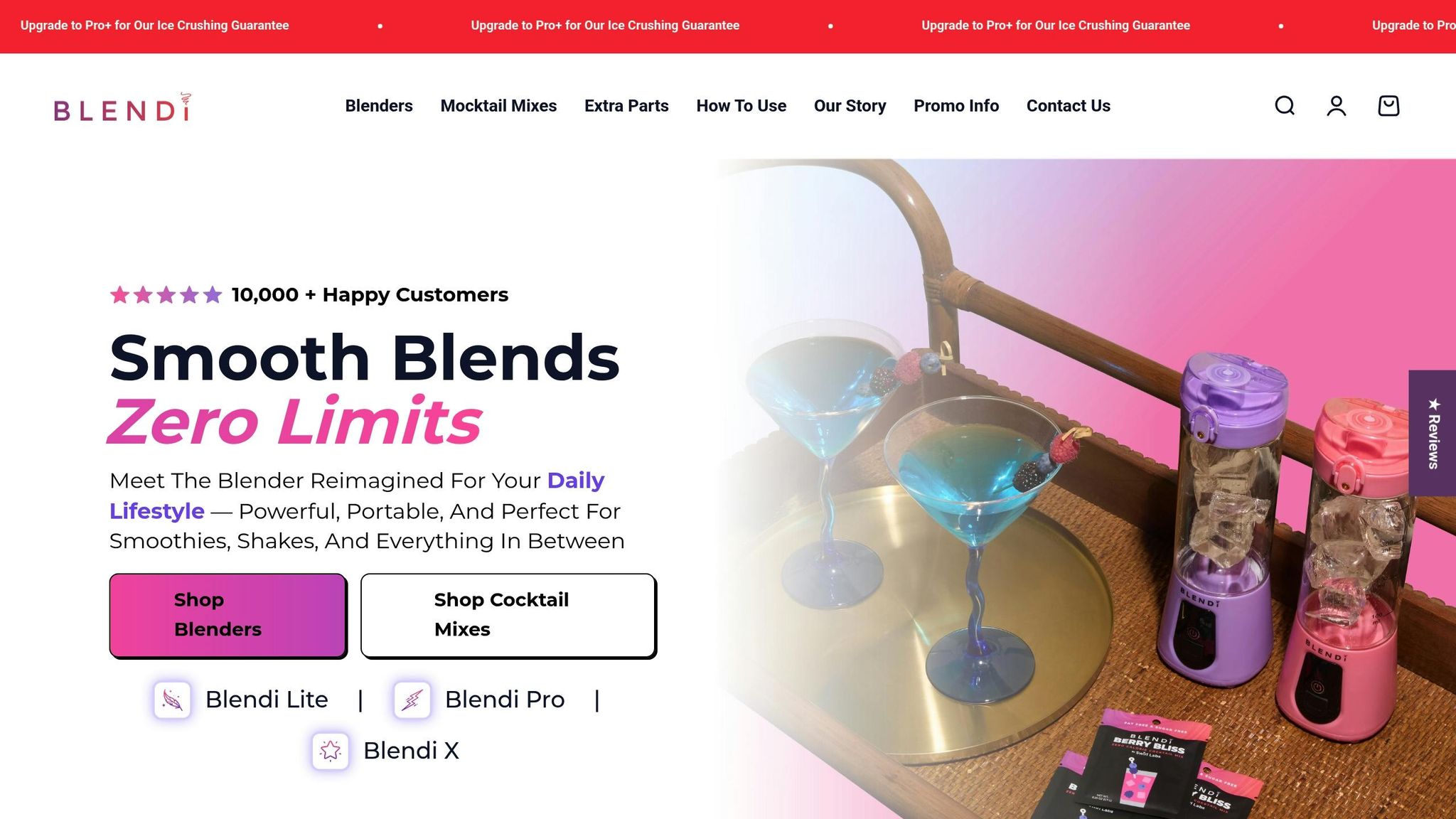
BLENDi is a standout example of a brand embracing these eco-friendly trends. Its product lineup focuses on durable, travel-friendly designs that cut down on single-use plastic waste. BLENDi’s portable blenders - like the BLENDi Lite, Pro+, and X models - are built for longevity and reusability. They even double as travel bottles, reducing the need for extra containers and helping users minimize their overall plastic consumption.
The brand goes beyond blenders, offering eco-conscious accessories like water bottles and travel cases. BLENDi also introduces zero-calorie mocktail mixers, providing a creative alternative to single-use beverage packaging by letting users make drinks on demand.
BLENDi’s multi-functionality design philosophy aligns with broader industry trends. Products that serve multiple purposes help reduce the number of items consumers need, which in turn decreases material use and waste. By incorporating advanced recycling processes, modular features, and transparent sourcing, BLENDi addresses the demand for products that last longer and generate less waste. With a focus on durability and repairability - highlighted by features like ice-crushing capabilities and sturdy construction - BLENDi ensures its products can handle regular use over time.
Switching to rPET instead of virgin PET is another win for the environment. It cuts energy use by up to 60% and greenhouse gas emissions by up to 50%. Every ton of recycled plastic used keeps thousands of bottles out of landfills and oceans, directly contributing to waste reduction. As these trends continue to grow, brands like BLENDi that emphasize durability, functionality, and waste reduction are well-positioned to meet the rising demand for sustainable drinkware solutions.
Conclusion: The Future of Recycled Plastic in Drinkware Design
Recycled plastics are reshaping drinkware design, offering more than just an eco-conscious alternative - they're redefining how we approach portable drinking solutions. Materials like rPET and recycled HDPE have proven they can match the quality of virgin plastics while significantly reducing environmental impact. For example, switching to recycled plastic can lower greenhouse gas emissions by up to 70%, demonstrating that these materials meet both performance and environmental expectations.
Thanks to advanced recycling technologies like depolymerization, even colored ocean plastics can now be transformed into food-grade drinkware. This innovation means manufacturers no longer face a trade-off between sustainability and quality - they can deliver both, paving the way for broader adoption of recycled materials.
Consumer interest in eco-friendly products has created a unique opportunity for brands to stand out by prioritizing sustainable materials. Shoppers are increasingly factoring environmental responsibility into their purchasing decisions, alongside functionality. This growing demand encourages companies to lead with designs that are not only practical but also environmentally conscious.
Take BLENDi's Pro+ and X models, for instance. These products combine durability, eco-friendliness, and multifunctionality, serving as both blenders and travel bottles. By reducing the need for multiple containers, BLENDi exemplifies the industry's move toward reusable and sustainable solutions.
The industry is also exploring new possibilities, such as ocean plastic recovery programs and closed-loop recycling systems. These efforts not only provide additional sources of recycled materials but also address the broader challenge of plastic pollution.
Continuous advancements in recycling infrastructure and quality control are addressing lingering challenges, ensuring that recycled materials meet consumer expectations. With clear labeling of recycled content and transparent sourcing practices, brands are building trust and encouraging wider adoption.
As recycling technologies improve and awareness grows, recycled plastic is becoming the new standard in drinkware. By investing in sustainable practices today, brands can secure long-term success in a market that increasingly values environmental responsibility without sacrificing quality.
FAQs
What are the environmental benefits of using recycled plastics like rPET and recycled HDPE in drinkware design?
Using recycled plastics like rPET (recycled polyethylene terephthalate) and recycled HDPE (high-density polyethylene) in drinkware brings a range of environmental advantages. For starters, these materials give discarded plastics a new purpose, keeping them out of landfills and oceans. Plus, producing items from recycled plastics generally consumes less energy than creating new, virgin plastics, which helps reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
Incorporating recycled plastics into drinkware also champions a more resource-conscious production cycle. Instead of depending on raw materials, this method prioritizes reusing what’s already available. The result? A reduced environmental footprint and fresh opportunities for eco-friendly, forward-thinking product design.
How is the safety and quality of drinkware made from recycled plastics ensured?
Manufacturers guarantee that drinkware made from recycled plastics is both safe and reliable by performing thorough testing to ensure the materials meet food-grade standards and contain no harmful chemicals. During production, they enforce rigorous quality control measures to identify and eliminate any contaminants or flaws.
Using recycled plastics helps cut down on waste while providing a sturdy and environmentally conscious choice for portable drinkware. By focusing on safety and responsible practices, brands create products that are practical and better for the planet.
What are the challenges of using recycled plastic in drinkware design, and how are they being overcome?
Using recycled plastic in drinkware design isn't without its hurdles. One major challenge is ensuring consistent material quality - recycled plastics often differ in color, texture, and composition, which can affect both the look and performance of the finished product. Durability and safety standards also need to be met, adding another layer of complexity.
To tackle these challenges, companies are turning to advanced recycling technologies and implementing strict quality control measures. These steps help ensure the production of reliable, environmentally conscious drinkware that doesn’t compromise on functionality. By rethinking how materials are sourced and processed, brands are finding ways to minimize environmental impact while still delivering the high-quality products consumers expect.




Leave a comment
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.